Which Of The Following Mechanisms Accounts For Supine Hypotensive Syndrome?
Which of the following mechanisms accounts for supine hypotensive syndrome?. Supine hypotension is compensated by an increase in peripheral sympathetic activity. The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus compresses the vagus nerve slowing the heart rate and decreasing cardiac output. We report a case of a 41yearold 39weekpregnant woman found dead supine.
The blood pressure measured in the arms is a reliable predictor of uterine and placental blood flow when the patient is supine. Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine symptoms and hypotension in late pregnancy which compel the unconstrained subject to change position. 1995-11-01 000000 In 1947 when a member of the newly established Department of Anaesthetics at the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary under Dr John Gillies I was asked to cover the anaesthetic service to the Simpson Memorial Maternity Pavilion in addition to my full-time duties in the surgical hospital.
Rarely it may manifest even from the fifth month of pregnancy or postpartum as well as in the pelvic tilt or sitting positions. Up to 70 of patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension nOH have associated supine hypertension. Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine symptoms and hypotension in late pregnancy which compel the unconstrained subject to change position.
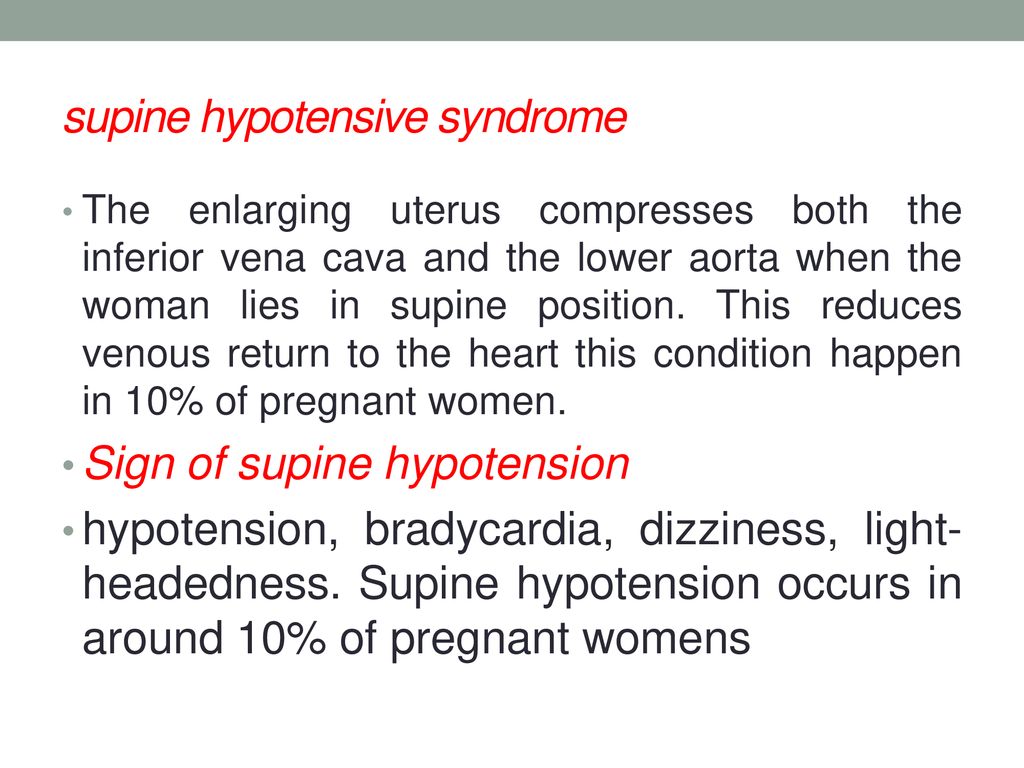
Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine hypotension in late pregnancy whose clinical presentation ranges from minimal cardiovascular alterations to severe shock resulting from inferior vena cava compression by gravid uterus. Supine positioning of a pregnant patient will result in aortocaval compression ACC. The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus compresses the descending aorta restricting blood flow to the rest of the body.
Hypercapnia decreased chest wall and lung compliance. 1 This may be due to a patients pre-existing neurodegenerative disorder and autonomic dysfunction including Parkinsons disease multiple system atrophy and pure autonomic failure. Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine hypotension in late pregnancy whose clinical presentation ranges from minimal cardiovascular alterations to severe shock resulting from inferior vena cava compression by gravid uterus.
Aortocaval compression can reduce uterine perfusion due to reduced uterine venous pressure. 23 Patients with autonomic failure lack the normal blood pressure buffering mechanisms that offset both. SH may be associated by four patterns of hypotensive reactions on HUTT.
1 typical neurogenic OH 16 characterised by the sudden and severe drop in BP within three minutes of head up tilt associated with dizziness and light headedness or loss of consciousness fig 1. Hypotension decreased cardiac output.
Which of the following mechanisms accounts for supine hypotensive syndrome.
The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus presses on the inferior vena cava causing inadequate blood return to. Secondly cardiac output can be reduced by aortocaval compression when some mothers lie in the supine position although this is not necessarily clinically evident. Increased airway pressure. Which of the following mechanisms accounts for supine hypotensive syndrome. The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus presses on the inferior vena cava causing inadequate blood return to. The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus compresses the descending aorta restricting blood flow to the rest of the body. Rarely it may manifest even from the fifth month of pregnancy or postpartum as well as in the pelvic tilt or sitting positions. Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine hypotension in late pregnancy whose clinical presentation ranges from minimal cardiovascular alterations to severe shock resulting from inferior vena cava compression by gravid uterus. The weight of the enlarged uterus and fetus compresses the vagus nerve slowing the heart rate and decreasing cardiac output.
Supine hypotensive syndrome is characterized by severe supine hypotension in late pregnancy whose clinical presentation ranges from minimal cardiovascular alterations to severe shock resulting from inferior vena cava compression by gravid uterus. Hypotension decreased cardiac output. Hypercapnia decreased chest wall and lung compliance. However up to 15 of women at term can demonstrate supine hypotensive syndrome of pregnancy defined as a decrease in systolic blood pressure of at least 1530 mmHgThe syndrome has been demonstrated in pregnant females from the middle of the second trimester onward. Deteriorating O2 A-a gradients due to increased raised diaphragm and atelectasis increased intrapulmonary shunt VQ mismatch. Which of the following mechanisms accounts for supine hypotensive syndrome. Increased airway pressure.





































Post a Comment for "Which Of The Following Mechanisms Accounts For Supine Hypotensive Syndrome?"