Treatment Of Hoarseness After Intubation
Treatment of hoarseness after intubation. Hoarseness after any of these surgeries may be temporary or permanent due to vocal fold immobility. Little however has been reported regarding laryngeal injury from short-term intubation. Analysis of 54 patients complaining of hoarseness after tracheal intubation.
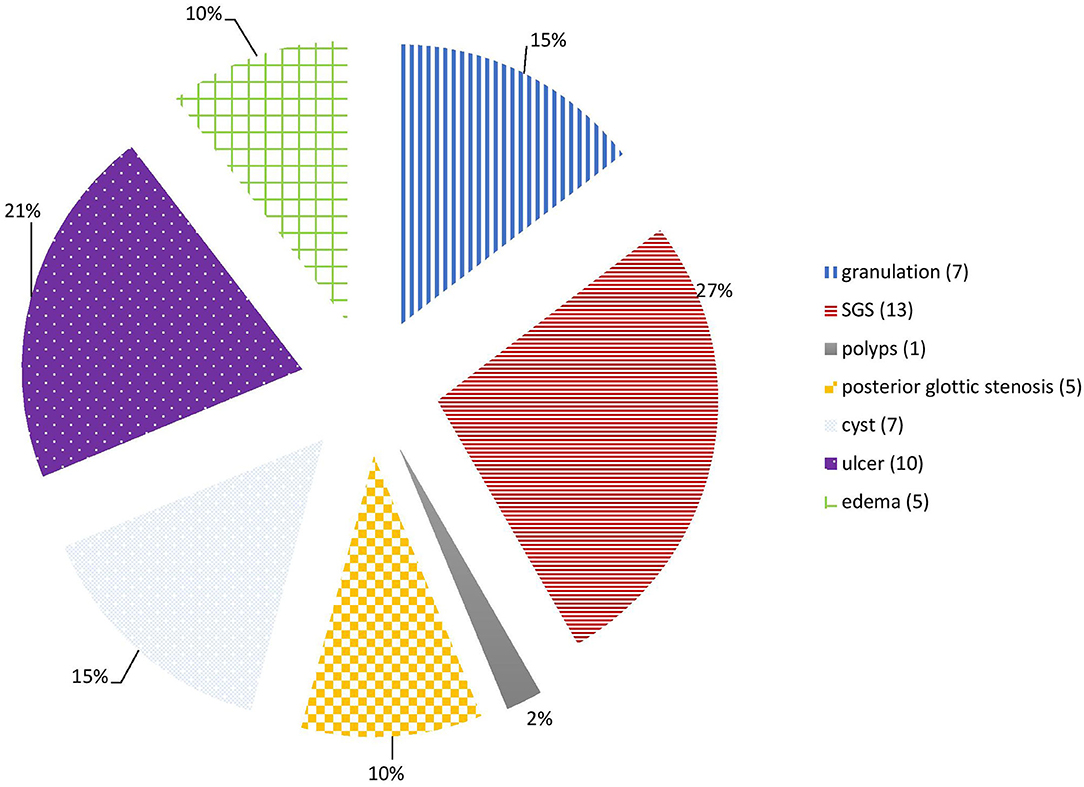
14 However patients usually consult an otorhinolaryngologist only if postoperative hoarseness persists for a longer time eg 6 weeks since. There is no study therefore that categorically demonstrates that the use of lubricating jelly containing a local anaesthetic is beneficial in the reduction of postoperative sore throat after tracheal intubation. In case of persistent hoarseness after endotracheal intubation clinicians should suspect arytenoid cartilage subluxationdislocation as a complication of intubation.
Contributing factors include the size of the tube cuff design and pressure variation in skills and techniques between anaesthesiologist and the subjectivity of the symptom of sore throat in individual patients. If postoperative hoarseness was still present on postoperative day 7 the patient was followed up until complete resolution. Treatment options include vocal cord injection injection laryngoplasty vocal cord medialization laryngoplasty thyroplasty Isshiki type I thyroplasty.
If you use an inhaler rinse your mouth after use. Keep your vocal cords well hydrated. The main treatment of intubation-related laryngeal granulomas is microlaryngeal surgical excision but low dose radiotherapy and other drugs such as corticosteroids botulinum toxin and zinc sulfate are also used in support to treat related symptoms or manage granuloma recurrence.
It is unclear what the basis may be for the common findings of hoarseness and discomfort after intubation. Avoid hot dry environments. Closed reduction is a safe and effective treatment method for arytenoid dislocation.
This study was conducted to evaluate whether the perioperative use of Strepsils lozenges would reduce the incidence of postoperative sore throat and hoarseness. 4812 It may have a negative effect on the patients degree of satisfaction as well as on their level of activity after hospital discharge. Toxin injections for the treatment of hoarseness caused by adductor spasmodic dysphonia.
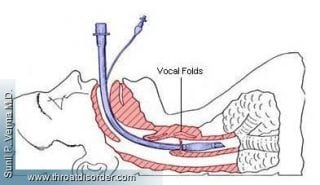
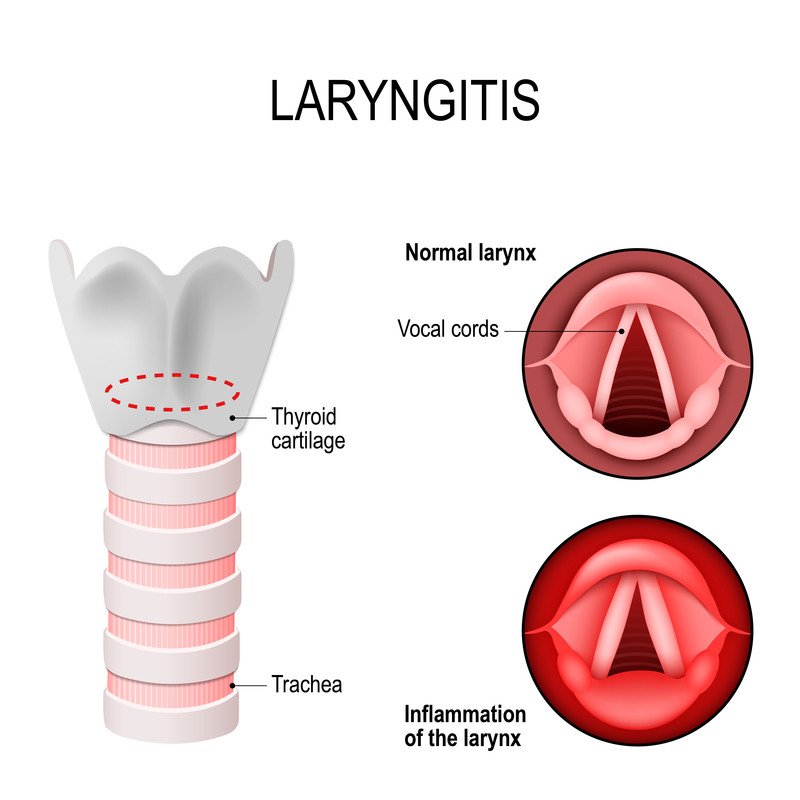
Postoperative hoarseness an important clinical sign of laryngeal injury or dysfunction can be distressing to a patient. This is opposed to tracheal intubation where the breathing tube passes through the vocal cords.
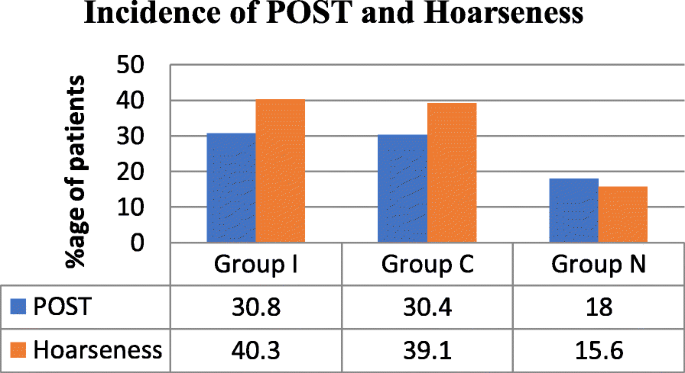
Of post-operative sore throat after tracheal intubation varies from 14 to 50 so also hoarseness.
Contributing factors include the size of the tube cuff design and pressure variation in skills and techniques between anaesthesiologist and the subjectivity of the symptom of sore throat in individual patients. It is unclear what the basis may be for the common findings of hoarseness and discomfort after intubation. The incidence of laryngopharyngeal symptoms after endotracheal intubation varies between 57 and 90. Try drinking two litres of water a. We evaluated age gender weight Cormack grades duration of intubation and the anaesthetic agents used as factors affecting the duration of hoarseness after tracheal intubation. The panel offered as options that 1 the clinician may perform laryngoscopy at any time in a patient with. Even if temporary voice problems after these surgeries may be alleviated with a vocal fold injection which works immediately. Injection of the vocal cords is easily performed in the office setting in the unsedated patient. Contributing factors include the size of the tube cuff design and pressure variation in skills and techniques between anaesthesiologist and the subjectivity of the symptom of sore throat in individual patients.
If postoperative hoarseness was still present on postoperative day 7 the patient was followed up until complete resolution. Analysis of 54 patients complaining of hoarseness after tracheal intubation. 14 However patients usually consult an otorhinolaryngologist only if postoperative hoarseness persists for a longer time eg 6 weeks since. The main treatment of intubation-related laryngeal granulomas is microlaryngeal surgical excision but low dose radiotherapy and other drugs such as corticosteroids botulinum toxin and zinc sulfate are also used in support to treat related symptoms or manage granuloma recurrence. If postoperative hoarseness was still present on postoperative day 7 the patient was followed up until complete resolution. Hoarseness was observed in 49 of patients on the day of surgery and in 29 11 and. This is opposed to tracheal intubation where the breathing tube passes through the vocal cords.

/mouth-and-throat-care-after-surgery-3156877-FINAL-01ffe771ef1d49d5a59be53f945f8731.png)





/why-does-my-throat-hurt-after-surgery-3157316-v1-5c1abec1c9e77c00016f80e9.png)



















/intubation-021-5a299722e258f8003693b043.png)










Post a Comment for "Treatment Of Hoarseness After Intubation"