What Is Colitis And Celiac Disease
What is colitis and celiac disease. In a limited study in Australia it was found that out of 10 people who had been diagnosed with collagenous colitis and who had small intestinal biopsies celiac disease was found in 4 of the 10 patients which is a very high correlation1 At the time. Whereas the Crohns disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the. The type of damage is can also be different and varies with the type of colitis.
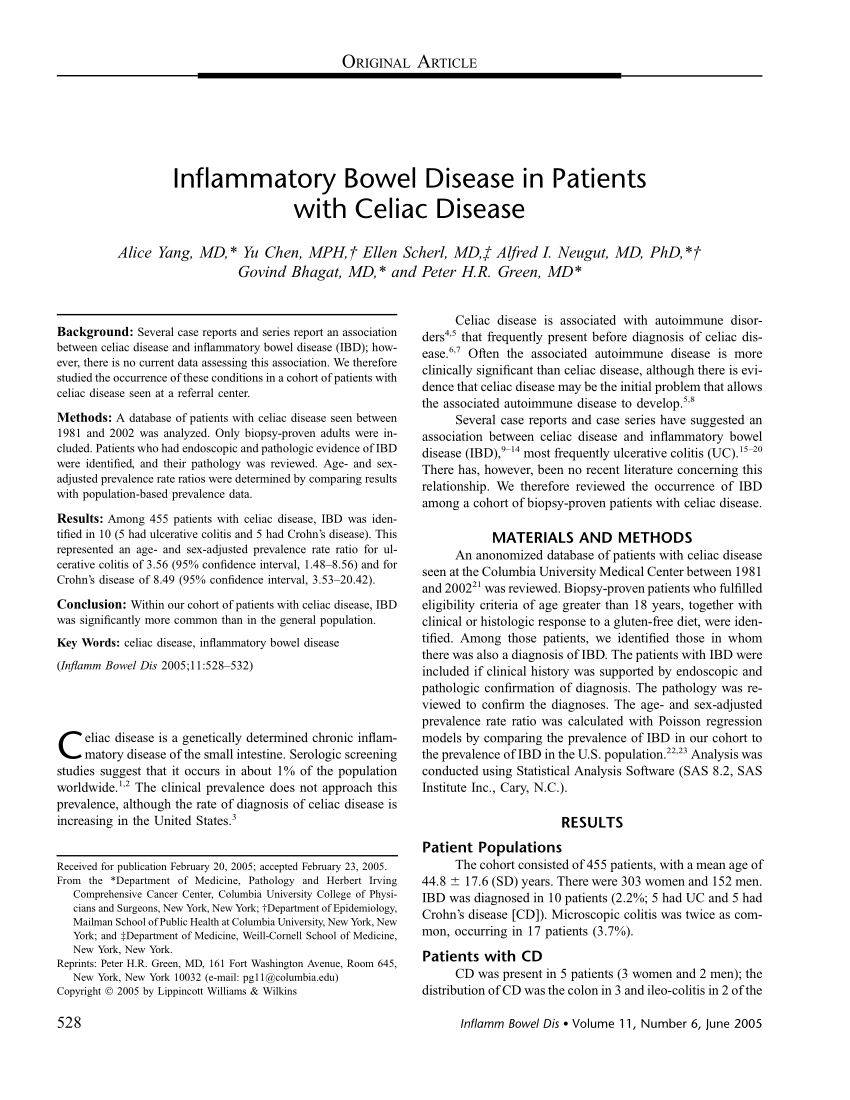
19791 with ulcerative colitis. We included 41482 adult IBD patients 20357 with Crohns disease. Also celiac disease is considered an immune disorder that significantly affects the patients life and lifestyle where IBS is not an immune disorder.
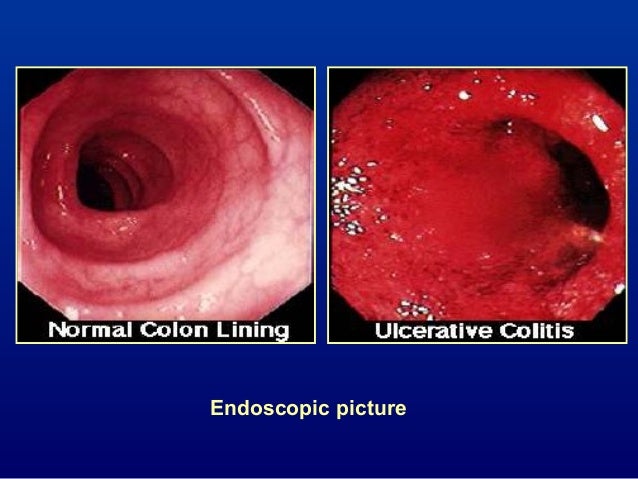
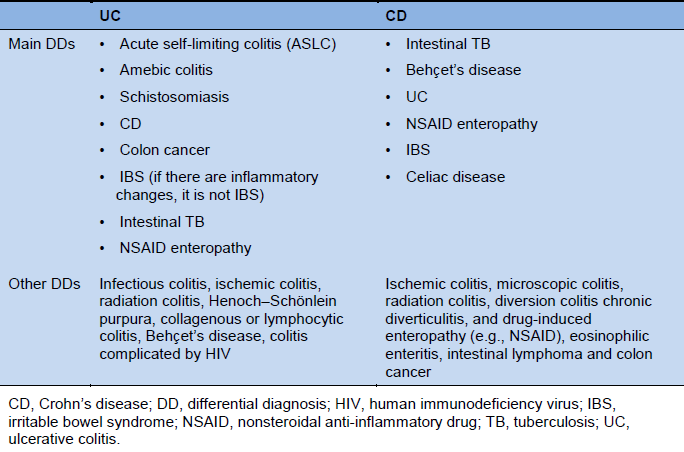
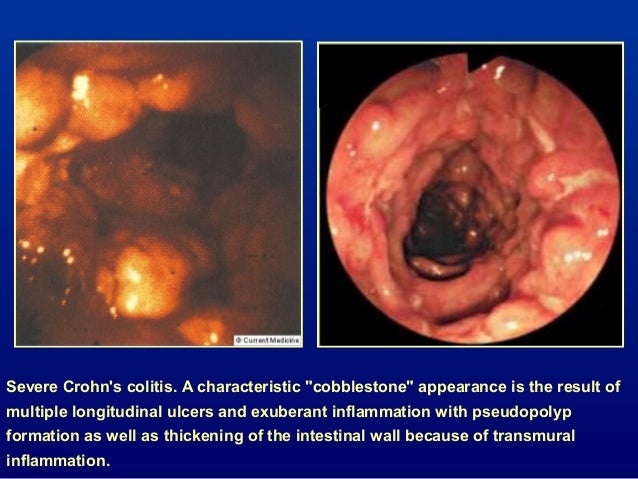
Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are the two main forms of inflammatory bowel diseases. Overlapping symptoms between Crohns disease and celiac disease include abdominal pain diarrhea anemia and short stature. And 459 patients with celiac disease.
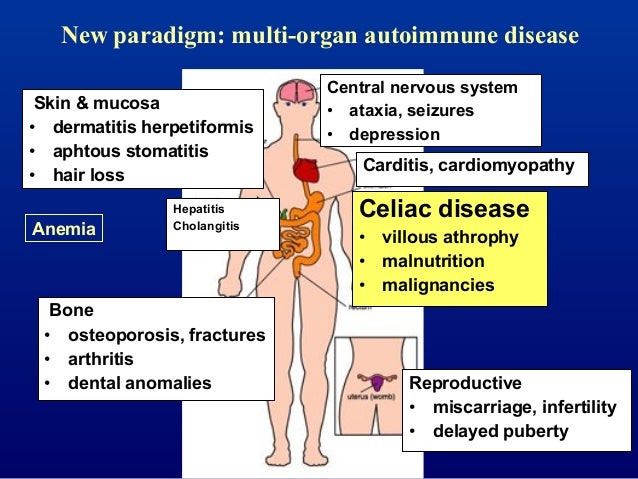
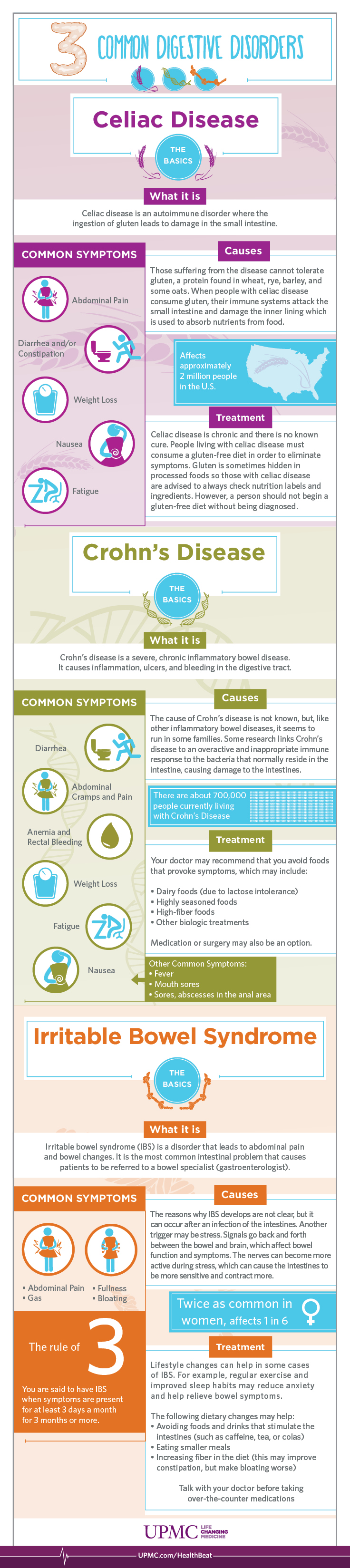
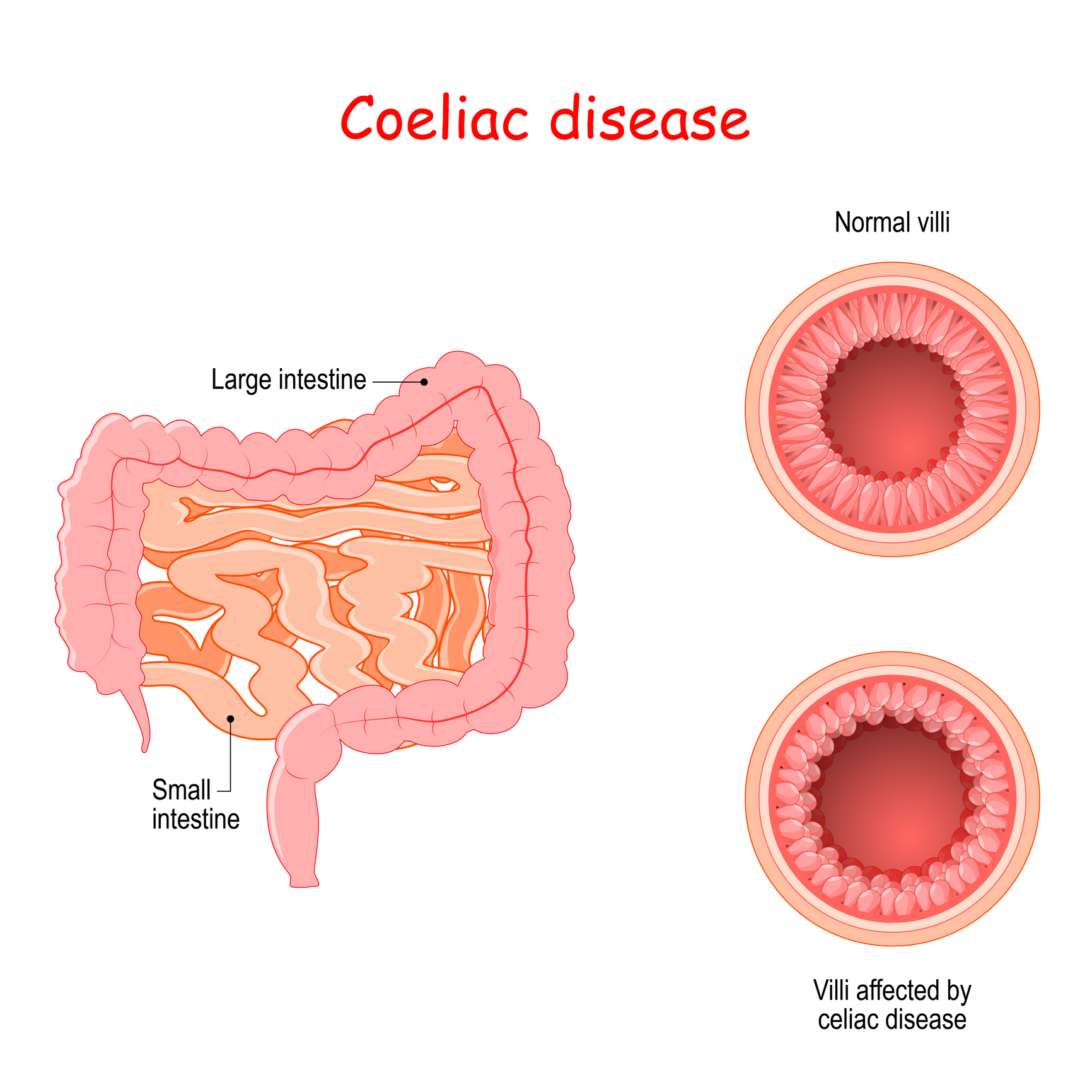
I t results in villus atrophy and malabsorption. Symptoms vary with the area of the GI tract that is being affected and usually begin between the ages of 13 and 30. The main difference between Celiac and Crohns disease is that the Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that can occur among genetically predisposed people where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine.
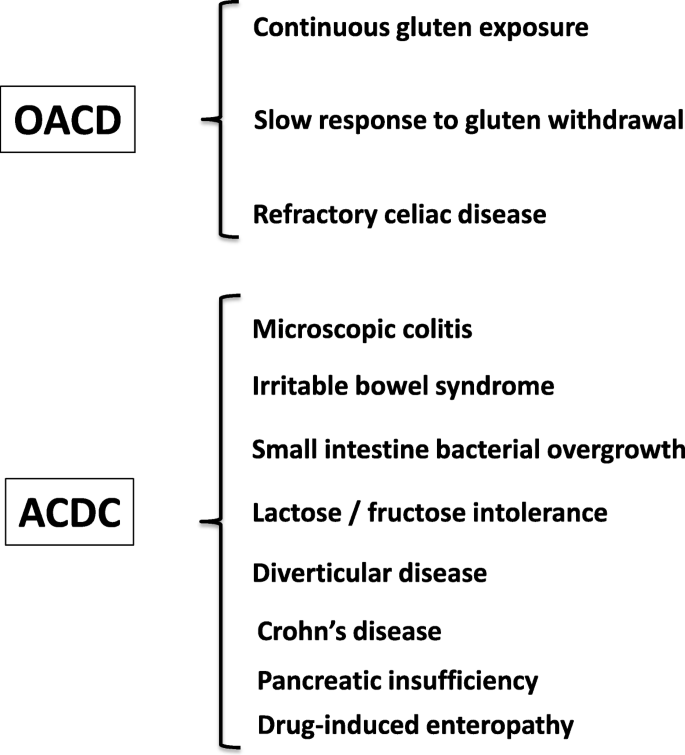
Crohns disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract. Celiac disease is a disease in which the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten leading to difficulty in digesting food. There seems to be a significant amount of overlap between microscopic colitis and celiac disease.
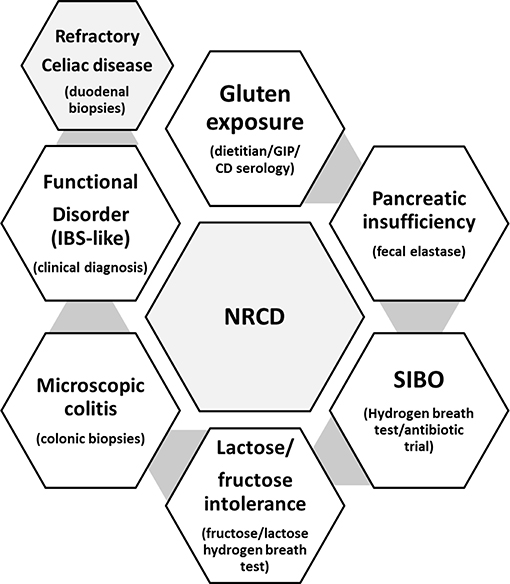
Verdu added that this means doctors could consider testing for celiac disease in a patient with IBD who remains symptomatic despite resolving colitis inflammation of the large intestine. People with celiac disease have an increased incidence of microscopic colitis and inflammatory bowel disease Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Celiac disease affects the small intestine and damages the villi making your body unable to absorb nutrients.
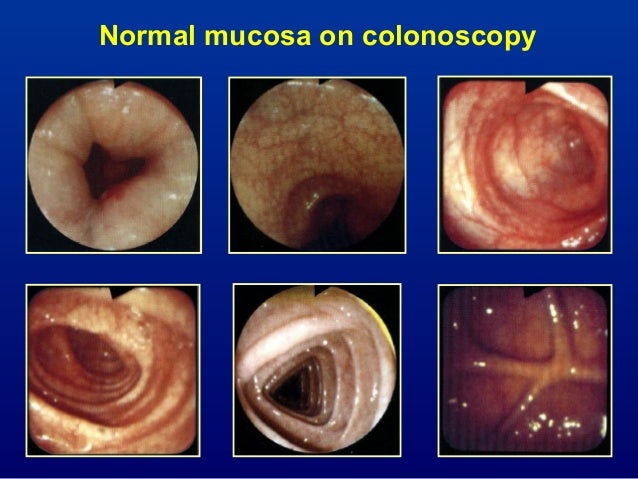
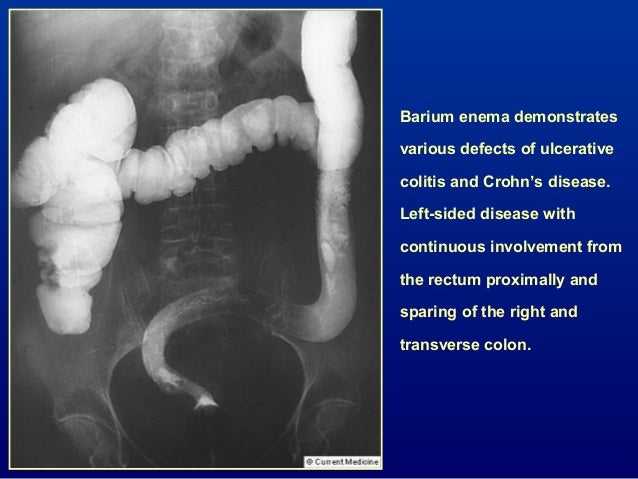
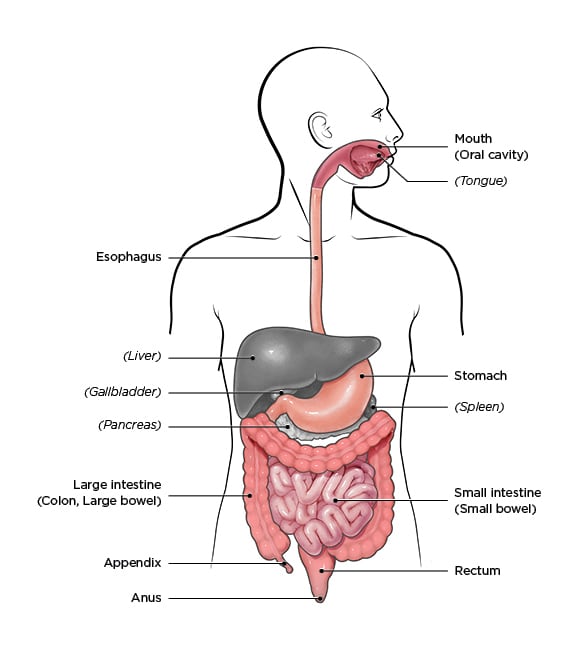
Microscopic colitis is an inflammation of the colon or large intestine. As a broad generalization colitis affects the large intestine and celiac affects the small intestine.
Also celiac disease is considered an immune disorder that significantly affects the patients life and lifestyle where IBS is not an immune disorder.
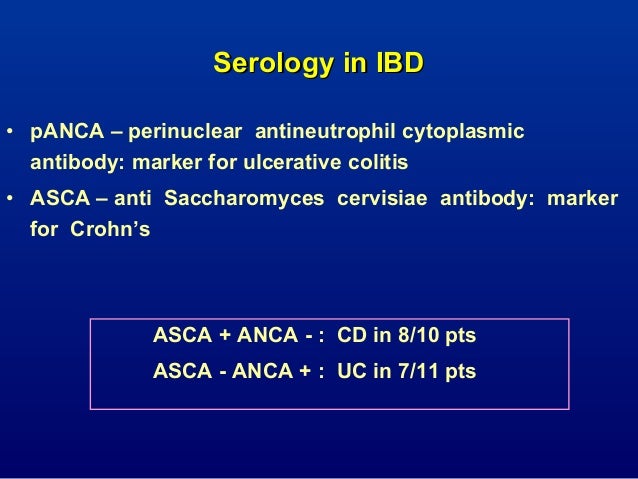
Celiac disease symptoms can mirror symptoms of gallbladder disease which is why many people who actually have celiac disease find themselves diagnosed with gallbladder problems. All of these conditions are characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract. Research shows that people with celiac disease also seem to be at an increased risk for inflammatory bowel disorders specifically Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis compared with. Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disease that occurs in genetically predisposed people where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. Microscopic colitis is an inflammation of the colon or large intestine. Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are the two main forms of inflammatory bowel diseases. Celiac Disease is an immune reaction to the consumption of gluten a protein found in wheat barley and rye. Given the genetic environmental and immune mechanisms both diseases share clinicians have for a long time believed there could be an association. Patients with celiac disease and microscopic colitis have more severe villous atrophy and frequently require steroids or immunosuppressant therapies to control diarrhea.
All of these conditions are characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract. An association between microscopic colitis and celiac disease Microscopic colitis is more common in patients with celiac disease than in the general population. Overlapping symptoms between Crohns disease and celiac disease include abdominal pain diarrhea anemia and short stature. Other symptoms include rectal bleeding weight loss. Symptoms vary with the area of the GI tract that is being affected and usually begin between the ages of 13 and 30. Another common culprit for misdiagnosis is colitis which shares many symptoms with celiac disease. I t results in villus atrophy and malabsorption.




















/IBD-Fuse-570d7da43df78c7d9e455a82.jpg)










Post a Comment for "What Is Colitis And Celiac Disease"